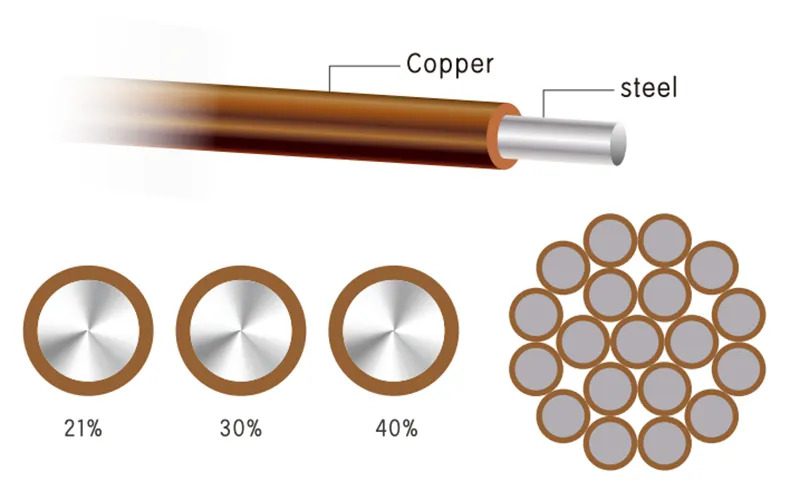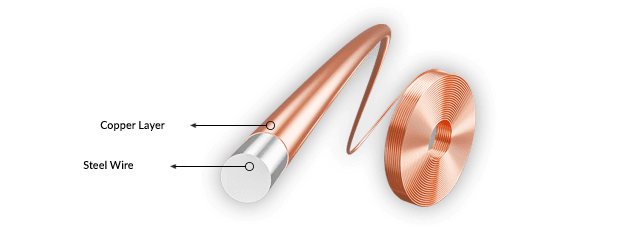
Copper-clad steel wire is a bimetallic composite. Manufacturers bond a conductive copper layer to a high-strength steel core wire. This process combines the best traits of both metals: the superior electrical conductivity of copper and the exceptional tensile strength of steel. The result is a versatile and high-performance material for demanding applications.
Structure and Core Properties
This wire has a unique dual-material design. A robust steel core forms the central backbone, providing mechanical support. A continuous copper sheath surrounds this core, ensuring excellent electrical contact. The steel core contributes high strength and resistance to high-temperature softening. Meanwhile, the copper cladding offers high conductivity, low contact resistance, and good corrosion resistance.
Key Characteristics
Copper-clad steel wire delivers a valuable set of advantages:
- High conduction efficiency
- Significant material cost savings
- High tensile breaking force
- Reduced weight
- Excellent wear resistance
Available Specifications
You can select this wire in various standard grades to meet project needs.
- Conductivity: It is commonly available at 21%, 30%, and 40% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard).
- Temper: Suppliers offer it in Soft (Annealed), Hard, and Extra-Hard states for different mechanical requirements.
Finishing Options
The base wire can undergo additional plating for enhanced performance. Common finishes include:
- Silver plating
- Tin plating
- Lead-tin alloy plating
These finishes improve solderability or provide better environmental resistance for specific uses.
Performance vs. Pure Copper
Copper-clad steel wire offers several key benefits over solid copper wire.
Superior High-Frequency Performance
In applications like RF and CATV systems, this wire demonstrates lower signal attenuation at high frequencies. This characteristic enables more efficient signal transmission.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
The steel core provides about twice the tensile strength of a solid copper wire in a comparable temper. This greater strength ensures higher reliability and a longer service life in harsh or dynamic environments.
Design and Economic Advantages
Engineers can tailor the wire’s properties to specific conductivity and strength needs, simulating various copper alloys. Economically, using a steel core reduces material costs by conserving copper. The final product is also lighter, which lowers transportation and installation expenses.
Industry Applications
This composite wire serves as an ideal solution across multiple sectors due to its balanced properties.
- Communications: Manufacturers use it in coaxial cable conductors for CATV and RF systems, where its skin effect performance is optimal.
- Power Transmission: The wire is common in grounding applications and stranded conductors, where both strength and conductivity are critical.
- Electronics: Its excellent solderability makes it a preferred choice for component lead wires, connectors, and terminals, and it suits automated assembly processes well.
Conclusion
Copper-clad steel wire represents a significant material innovation. It successfully balances performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. By merging the electrical qualities of copper with the mechanical strength of steel, it provides a sustainable and economical alternative to pure copper. Its wide use in communications, power, and electronics highlights its role as a critical material for modern industry.