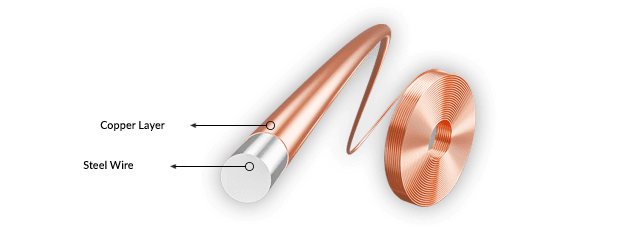
Copper clad steel (CCS) is a composite material that combines the core strength of steel with the electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance of copper. It is manufactured by permanently bonding a thick outer layer of copper to a steel core, typically through a metallurgical process such as cladding, electroplating, or continuous drawing. This creates a bi-metallic wire or rod that offers a unique set of properties.
The primary advantage of copper clad steel lies in its optimized performance-to-cost ratio. The steel core provides high tensile strength, durability, and reduced thermal expansion, making the composite wire mechanically robust and suitable for applications requiring long spans or resistance to stretching and breakage. Meanwhile, the copper outer layer ensures excellent electrical conductivity—though slightly lower than pure copper—and provides good solderability, corrosion resistance, and the familiar appearance of copper.
This combination makes CCS an ideal material for several key applications:
- Telecommunications and RF Grounding: It is widely used in coaxial cable center conductors (e.g., for cable TV), RF antennas, and grounding wires, where strength and adequate conductivity are crucial.
- Power Transmission & Grounding: CCS is employed in overhead power line grounding wires, subway rail bonds, and lightning protection systems.
- Automotive and Industrial Applications: It finds use in battery cables, control cables, and other scenarios where vibration resistance and durability are important.
In essence, copper clad steel is a versatile engineered material. It is not a perfect substitute for pure copper where maximum conductivity is essential, nor for pure steel where maximum strength is the sole concern. However, it provides an excellent and economical solution where a balance of mechanical strength, electrical performance, corrosion resistance, and cost is required.
