Copper-clad steel wire offers a unique combination of properties. Specifically, it bonds a conductive copper layer to a strong steel core. Consequently, this balance makes it a popular choice for power transmission and other electrical applications. Among various types, the 7-strand and 19-strand constructions are common, as each meets different engineering needs.
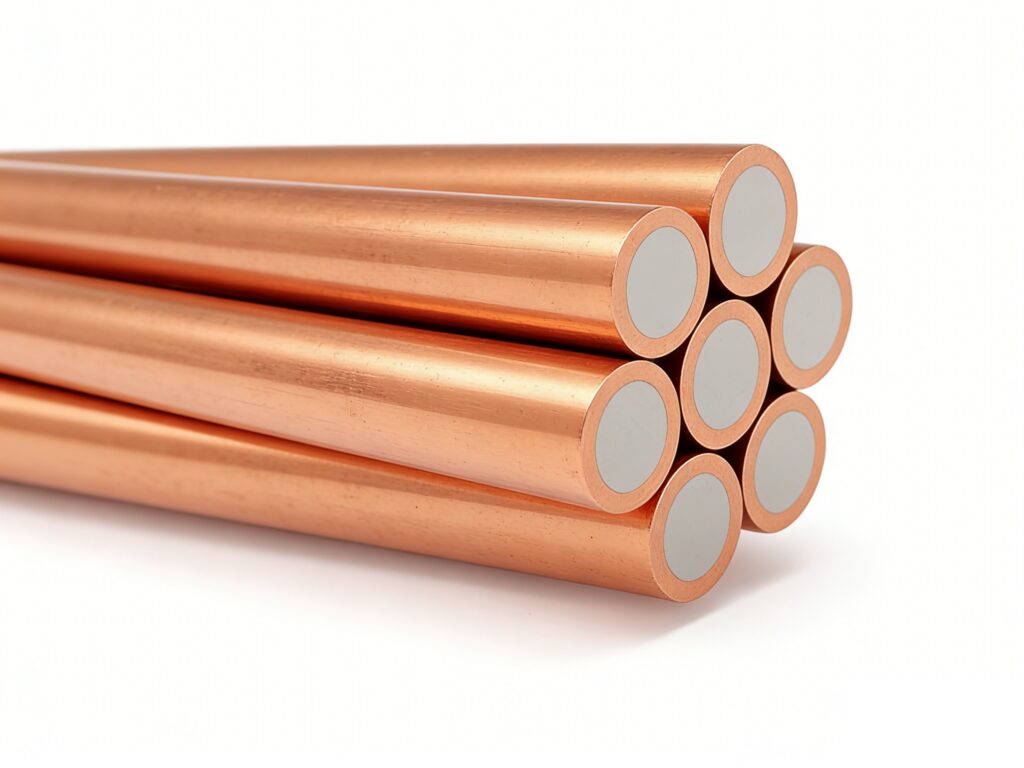
7-Strand Copper-Clad Steel Wire
The 7-strand wire is made by twisting seven individual wires together. As a result, it balances flexibility, strength, and weight well.
- Structure and Characteristics: First, this design provides excellent flexibility. Meanwhile, it also has sufficient tensile strength. Furthermore, its smaller diameter and lighter weight ease installation. This is particularly useful in complex terrain.
- Key Advantages and Applications: Due to good resistance to wind-induced motion and ease of installation, 7-strand wire is common in medium- to short-span overhead lines and distribution networks. Additionally, it is reliable for grounding systems, transformer leads, and substation connections.
19-Strand Copper-Clad Steel Wire
The 19-strand wire uses nineteen finer individual wires, representing a higher-performance solution.
- Structure and Enhanced Properties: More strands increase the surface area. More importantly, the structure is denser, thus granting higher tensile strength. It also has better fatigue resistance and, furthermore, enhanced corrosion resistance. Therefore, it can withstand greater tension and harsher conditions.
- Key Advantages and Applications: This wire is engineered for demanding uses. For example, it suits main transmission lines with long spans and high tension. Similarly, it is ideal for heavy ice-loading regions or high-corrosion coastal areas. In summary, its improved durability ensures long-term reliability.
Comparison and Selection Guide
Choosing between the two types requires evaluating project parameters:

Mechanical Requirements: For higher tension, longer spans, or ice loading, prioritize 19-strand wire. Conversely, for routine tensions needing flexibility, 7-strand wire is more cost-effective.
Environmental Factors: In highly corrosive areas, 19-strand wire typically gives better protection. However, in general environments, both work, but one must weigh strength versus cost.
Electrical and Installation Considerations: Both meet conductivity standards. However, 7-strand wire is lighter and more flexible, thus easing installation. In contrast, 19-strand wire is slightly more complex to install but has a longer life and, simultaneously, lower maintenance costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both wire types are foundational for modern power systems. The 7-strand wire is practical, flexible, and economical. Meanwhile, the 19-strand wire offers superior strength and durability. Therefore, utility companies should choose based on specific distance, tension, environment, and cost goals. This approach ultimately ensures optimal system performance, safety, and economy.
